How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from capturing breathtaking aerial photography to conducting professional inspections. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical skill and responsible awareness. This guide will walk you through the essential steps, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight techniques and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you can confidently take to the skies.
We’ll cover everything from understanding your drone’s controls and navigating different flight modes to optimizing camera settings for stunning visuals and managing battery life effectively. We’ll also delve into important safety regulations and best practices to ensure responsible and legal operation. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone safely and efficiently, unlocking its full potential.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves checking various components of your drone and understanding relevant regulations. A safety briefing is also essential, particularly for novice pilots.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight check minimizes the risk of malfunctions and accidents. The following table Artikels key components and their acceptable/unacceptable conditions:
| Component | Check | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or imbalance. | No visible damage, securely attached. | Cracks, chips, significant wear, loose attachment. |
| Motors | Visually inspect for damage and ensure smooth rotation. | No visible damage, spins freely without resistance. | Visible damage, binding, unusual noises during rotation. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition. | Sufficient charge, no visible damage or swelling. | Low charge, visible damage, swelling. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and proper alignment. | Moves smoothly and accurately, no binding or unusual noises. | Stiff movement, jerky operation, misalignment. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal before takeoff. | At least 8 satellites acquired, good signal strength. | Weak signal, less than 6 satellites acquired. |
Understanding Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires adherence to local regulations and airspace restrictions. Ignoring these rules can lead to legal consequences and safety hazards. Common restrictions include no-fly zones near airports, stadiums, and other sensitive areas. Many countries utilize apps that clearly display restricted airspace.
For example, many countries prohibit drone flights above a certain altitude without special permission, and flights near populated areas may require additional authorization. Always check the latest regulations before flying in any location.
Safety Briefing for First-Time Drone Operators
A comprehensive safety briefing is vital for first-time drone operators. This briefing should cover emergency procedures, risk mitigation, and responsible drone operation. Emphasis should be placed on understanding the drone’s limitations and potential hazards.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
- Never fly near people or property without permission.
- Be aware of wind conditions and avoid flying in strong winds.
- Know how to perform an emergency landing procedure in case of GPS signal loss or other malfunctions.
- Familiarize yourself with the drone’s return-to-home function.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation modes is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the functions of a typical drone controller and explains different flight modes.
Drone Controller Functions
Most drone controllers utilize two joysticks and several buttons to control various aspects of flight and camera operation.
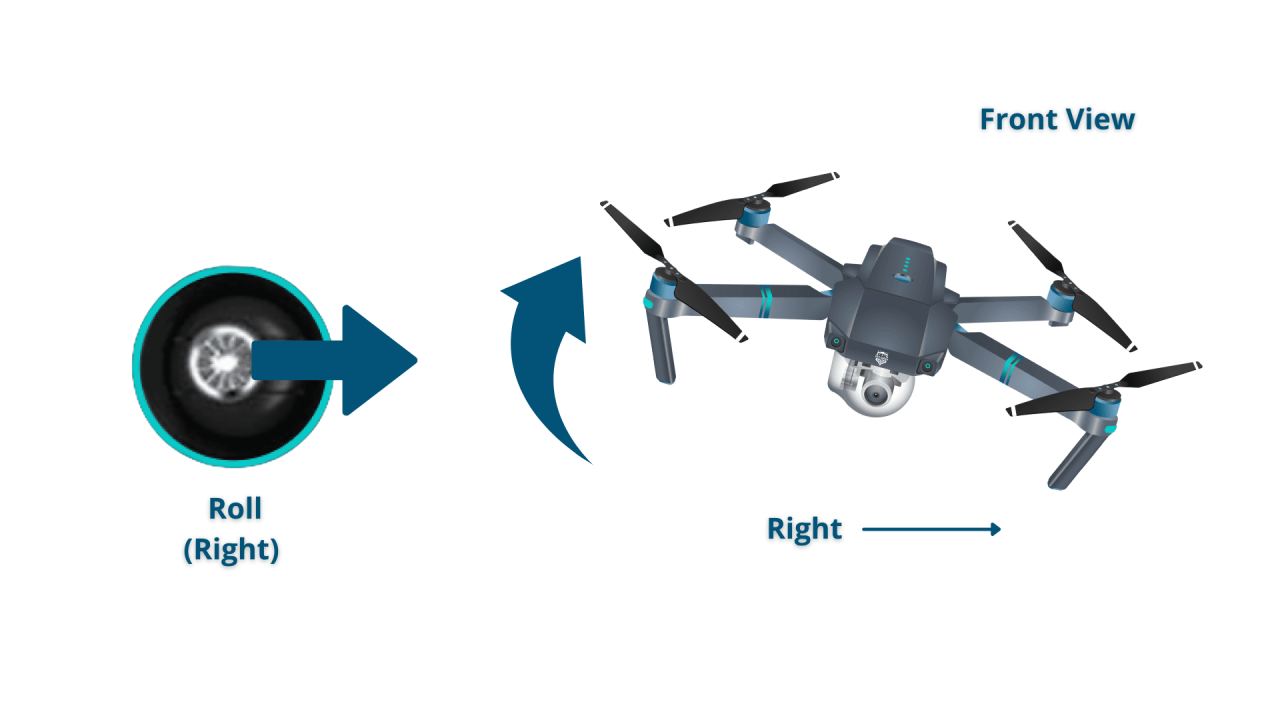
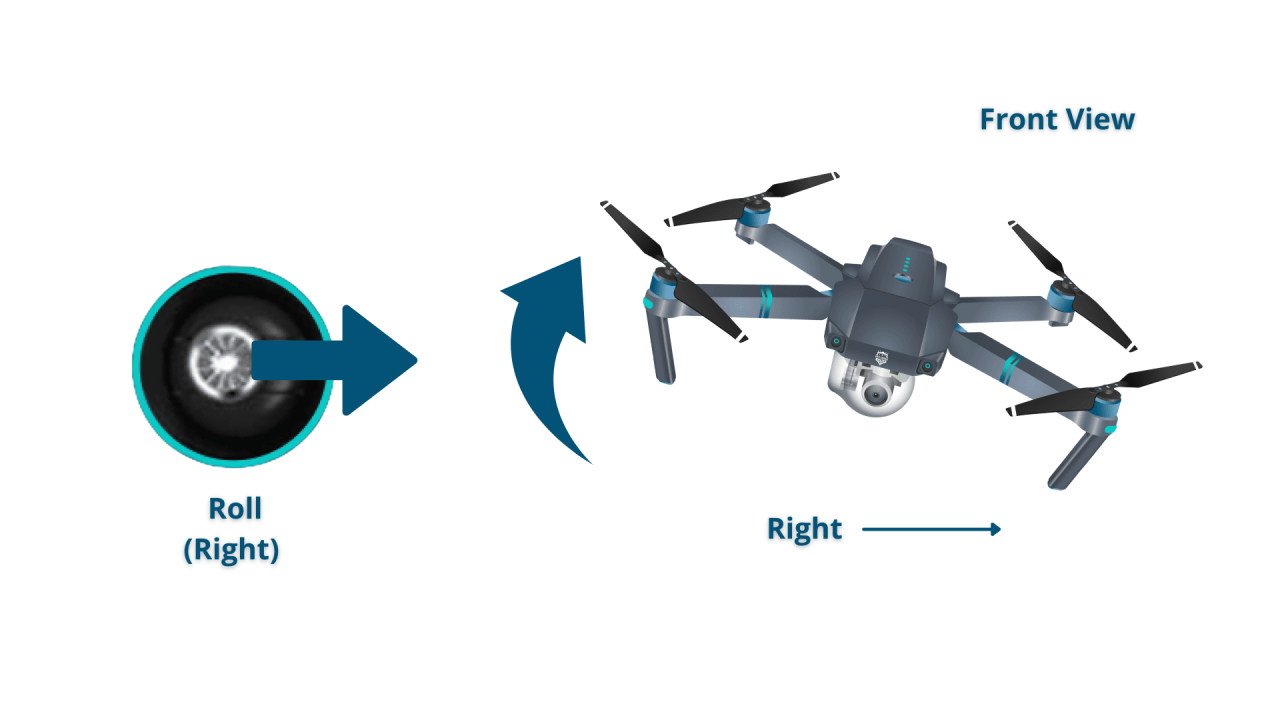
- Left Stick (Yaw and Throttle): Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and altitude (throttle).
- Right Stick (Pitch and Roll): Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the home point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Immediately cuts power to the motors, causing the drone to fall.
- Camera Control Buttons: Adjust camera settings such as zoom, photo/video recording, and gimbal movement.
Flight Modes: GPS Mode vs. Attitude Mode
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. GPS mode relies on satellite signals for precise positioning, while Attitude mode uses internal sensors for orientation.
| Flight Mode | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Excellent stability, precise hovering, automated features (RTH). | Requires a strong GPS signal, can be affected by GPS interference. |
| Attitude Mode | Greater maneuverability, can be used in areas with weak GPS signal. | Less stable, requires more skill to control. |
Step-by-Step Drone Flight Guide
- Pre-flight checks: Complete the pre-flight checklist.
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate takeoff.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable altitude by keeping the left stick centered.
- Movement: Use the right stick to control movement in different directions.
- Landing: Slowly lower the left stick to descend and land gently.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial images and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and best practices for framing and composition. This section covers camera settings and shot composition techniques.
Best Practices for Aerial Photography and Videography
Achieving compelling aerial footage involves careful consideration of shot composition, perspective, and lighting. Different shot types can enhance storytelling and visual impact.
- Wide Shots: Establish the overall scene and context.
- Close-ups: Highlight details and specific elements.
- Tracking Shots: Follow a moving subject or reveal a scene gradually.
- Aerial Panoramas: Capture sweeping views of landscapes.
Understanding Drone Camera Settings

Adjusting camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture affects image quality and exposure. Understanding these settings is crucial for capturing optimal footage in various lighting conditions.
| Setting | Description | Impact on Image Quality |
|---|---|---|
| ISO | Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. | Higher ISO values increase sensitivity (useful in low light) but can introduce noise. |
| Shutter Speed | Controls the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. | Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur. |
| Aperture | Controls the size of the lens opening. | Wider apertures (lower f-numbers) allow more light and create shallower depth of field. |
Optimizing Image Quality in Different Lighting Conditions
Adjusting camera settings based on lighting conditions ensures optimal image quality. In bright sunlight, reduce ISO and shutter speed to avoid overexposure. In low light, increase ISO and use a slower shutter speed, while being mindful of potential noise.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. Successfully navigating the skies requires practice and a good understanding of airspace regulations. For a comprehensive guide on the intricacies of piloting, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering how to operate a drone safely and effectively is key to enjoying this exciting technology responsibly.
Battery Management and Flight Time
Proper battery management is essential for maximizing drone flight time and extending battery lifespan. This section covers charging, storage, and factors influencing flight duration.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as pre-flight checks and maneuvering techniques, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide on all aspects of flight, including advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. Mastering these skills will ensure safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Proper Charging and Storage of Drone Batteries
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow their instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries completely. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Several factors influence how long your drone can stay airborne. These factors interact to determine the overall flight time.
| Factor | Effect on Flight Time |
|---|---|
| Wind Speed | Higher wind speeds reduce flight time due to increased energy consumption. |
| Payload (Camera, Gimbal, etc.) | Heavier payloads increase energy consumption, reducing flight time. |
| Battery Health | Older or damaged batteries have reduced capacity, resulting in shorter flight times. |
| Temperature | Extreme temperatures (hot or cold) can negatively impact battery performance and flight time. |
Optimizing Battery Usage for a Given Mission
Planning a flight mission involves considering factors like travel time and image capture to optimize battery usage. For example, a mission requiring extensive filming may need multiple batteries to complete successfully.
Consider shorter flights with frequent battery changes instead of pushing a single battery to its limits. This helps prevent unexpected mid-flight power failures.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their troubleshooting steps is crucial for resolving issues efficiently and preventing future problems. This section Artikels common problems and their solutions.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Their Causes
Several factors can cause drone malfunctions. Identifying the cause allows for targeted troubleshooting.
- GPS Signal Loss: Obstructions, interference, or weak signal strength.
- Low Battery: Insufficient charge or battery damage.
- Motor Failure: Mechanical damage, overheating, or electronic malfunction.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Mechanical issues, software glitches, or sensor problems.
- Propeller Damage: Bent, cracked, or loose propellers.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Malfunctions
Addressing drone malfunctions requires systematic troubleshooting. Start with simple checks and escalate as needed. Consult your drone’s manual for detailed instructions.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with a clear view of the sky, restart the drone.
- Low Battery: Replace the battery with a fully charged one.
- Motor Failure: Inspect motors for damage, ensure proper connections.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Check for physical obstructions, calibrate the gimbal, restart the drone.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
Preventative Measures to Minimize Drone Malfunctions
Regular maintenance and careful operation significantly reduce the likelihood of malfunctions.
- Regularly inspect the drone for any damage.
- Always use the manufacturer-recommended batteries and charger.
- Avoid flying in extreme weather conditions.
- Properly store the drone and its accessories when not in use.
Post-Flight Procedures
Post-flight procedures are equally important as pre-flight checks. They ensure the safe storage of the drone and its components, and the proper management of captured data.
Comprehensive Post-Flight Drone Inspection
After each flight, a thorough inspection is crucial to identify potential issues early on.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check motors for overheating or damage.
- Examine the drone’s body for scratches or dents.
- Verify the camera and gimbal are functioning correctly.
- Check battery levels and condition.
- Download and back up flight data and captured media.
Proper Storage of the Drone and Accessories
Store the drone and its accessories in a clean, dry, and safe place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. This helps to preserve their lifespan and prevent damage.
Post-Flight Checklist

A comprehensive post-flight checklist ensures that all necessary steps are followed consistently after each flight.
- Complete post-flight inspection.
- Download and backup flight data and media.
- Clean the drone and accessories.
- Store the drone and accessories properly.
- Charge batteries according to manufacturer guidelines.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic drone operation, exploring advanced techniques can significantly enhance your aerial photography and videography capabilities. This section explores more sophisticated flight maneuvers and functionalities.
Smooth and Controlled Drone Movements
Mastering precise hovering and tracking moving subjects requires practice and a good understanding of the drone’s controls and responsiveness. Smooth, controlled movements are essential for creating professional-looking footage.
Practice maintaining a stable hover in various wind conditions and gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers. Start with simple movements, then gradually incorporate more challenging techniques.
Utilizing Waypoint Navigation and Return-to-Home
Many drones offer waypoint navigation, allowing you to pre-program a flight path. This feature is useful for complex shots or when maintaining visual line of sight is difficult. The return-to-home (RTH) function provides an automated return to the takeoff point in case of GPS signal loss or other issues.
Practice setting waypoints in a safe and open area before attempting more complex maneuvers. Always maintain awareness of your surroundings and potential hazards.
Planning and Executing Complex Flight Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Planning complex flight maneuvers involves careful consideration of the drone’s capabilities, the environment, and potential risks. Always prioritize safety and adhere to all regulations.
Before attempting any complex maneuver, practice the individual components in a safe and controlled environment. Gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers as your skills improve. Always have a backup plan in case of unexpected issues.
Operating a drone is a rewarding experience, blending technology, skill, and creativity. By following the pre-flight and post-flight procedures, understanding the controls, and mastering the techniques Artikeld in this guide, you can safely and effectively utilize your drone for various applications. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Always prioritize safety and adhere to all local regulations.
Now, go explore the skies responsibly!
Questions and Answers
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes. Look for models with good reviews and ample online tutorials.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations in your region.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. If GPS is lost, activate RTH immediately, or carefully maneuver the drone back using visual references.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’ve been near strong magnetic fields.